Diagonal
diagonal.RmdHistogram
pairplot assumes that function passed to the three parts; diagonal, lower corner, upper corner eventual transformations do not affect the window differently, i.e the transformations do not create discrepancies of maximum and minimum value of transformed data across zones.
However, in some cases you may want to apply a transformation on the corners but not on the diagonal.
An example, would be rank transformation. Plotting an histogram of ranked transform data is not insightful, however plotting ranked transform data on corner plot can give an idea of monotonic degree between two variable rank, and thus gives insight whether two measures produce similar same ranking (visual analog to Spearman correlation). Plotting the histogram of the non-ranked transform data is also useful for having an idea of distribution of the data. One strategy, would be to feed the geom object to one of the corner with a custom stat which computes the rank of y-axis and x-axis. And map to the diagonal a histogram which operates directly on the original data. If there are 300 data points, the ranked data would lie in these boundaries and the corresponding plot grid boundaries of such data would be set to 0 and 300. pairplot corners have priority over diagonal for setting scale limits. Therefore, if the diagonal histogram operates on the 300 untransformed point values, with values lying between 0 and 1, the displayed histogram would be nearly not visible. As a result the diagonal mapped function has to consider its surrounding and has to be scaled to the upper and lower bounds of the near subplots.
Rather than trying to implement an automatic upper and lower bound detector function within internal function mapplot. I made the choice to let the user control. Diagonal functions can access surrounding subplot data. By adding diag_neighbour=c("t", "b", "l", "r") to pairgrid. The selected neighbour data will then be passed to the map_diag call under the form of a list: list(t=<ggplot_built>, b=<ggplot_built, ...) Returning to the example, we can leverage this argument in the function we pass to map_diag and set the histogram min-max scaling based on neighbour limits. This is already implemented in pair_grid_geom:
library(pairplot)
pair_geom_histogram
#> function (data, mapping, neighbour_ggdata = NULL, unit_y = FALSE,
#> stat = "bin", bins = 10, binwidth = function(x) {
#> bin_width_auto(x, na.rm = TRUE)
#> }, ...)
#> {
#> bin_width_value <- binwidth(data[[1]])
#> x = rlang::as_name(mapping$x)
#> if (unit_y) {
#> p <- ggplot(data = data, mapping = mapping) + geom_histogram(aes(y = ..ncount..),
#> stat = stat, bins = bins, binwidth = binwidth, ...)
#> }
#> else {
#> if (length(neighbour_ggdata)) {
#> for (key in c("t", "b")) {
#> xdata = neighbour_ggdata[[key]]
#> if (length(xdata)) {
#> break
#> }
#> }
#> for (key in c("l", "r")) {
#> ydata = neighbour_ggdata[[key]]
#> if (length(ydata)) {
#> break
#> }
#> }
#> xaxis_bounds <- if (length(xdata))
#> range(xdata$data[[1]]$x)
#> else {
#> c(min(data[x]), max(data[x]))
#> }
#> yaxis_bounds <- if (length(ydata))
#> range(ydata$data[[1]]$y)
#> else {
#> c(min(data[x]), max(data[x]))
#> }
#> lower_bound_y <- yaxis_bounds[1]
#> upper_bound_y <- yaxis_bounds[2]
#> lower_bound_x <- xaxis_bounds[1]
#> upper_bound_x <- xaxis_bounds[2]
#> t_data = min_max_scale(data[x], lower_bound_x, upper_bound_x)
#> p <- ggplot(data = t_data, mapping = mapping)
#> }
#> else {
#> p <- ggplot(data = data, mapping = mapping)
#> upper_bound_y <- max(data[x])
#> lower_bound_y <- min(data[x])
#> }
#> p <- p + geom_histogram(aes(y = after_stat((upper_bound_y -
#> lower_bound_y) * ((count - min(count))/(max(count) -
#> min(count))) + lower_bound_y)), stat = stat, bins = bins,
#> binwidth = binwidth, ...)
#> }
#> return(p)
#> }
#> <bytecode: 0x55deeeed6b38>
#> <environment: namespace:pairplot>Now, let’s see what happens when we do not use this feature. We compute the scatter and geom smooth of rank transformed variable. We use internal functions geom_point_rank() & geom_smooth_rank() to compute the lower corner plots.
:
library(ggplot2)
penguins_url <- "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/allisonhorst/palmerpenguins/main/inst/extdata/penguins.csv"
columns <- c("bill_length_mm", "bill_depth_mm", "flipper_length_mm", "body_mass_g")
penguins <- read.csv(penguins_url)[columns]
penguins <- penguins[!apply(is.na(penguins), 1, any), ] # dropping NA
pair_geom_rank_smooth <- function(data, mapping, formula=y~x, method="loess", ...) {
p <- ggplot(data = data, mapping = mapping) +
geom_point_rank() +
geom_smooth_rank(formula = formula, method=method, ...)
return(p)
}
pair_geom_rank_smooth(penguins, aes(x=flipper_length_mm, y=body_mass_g))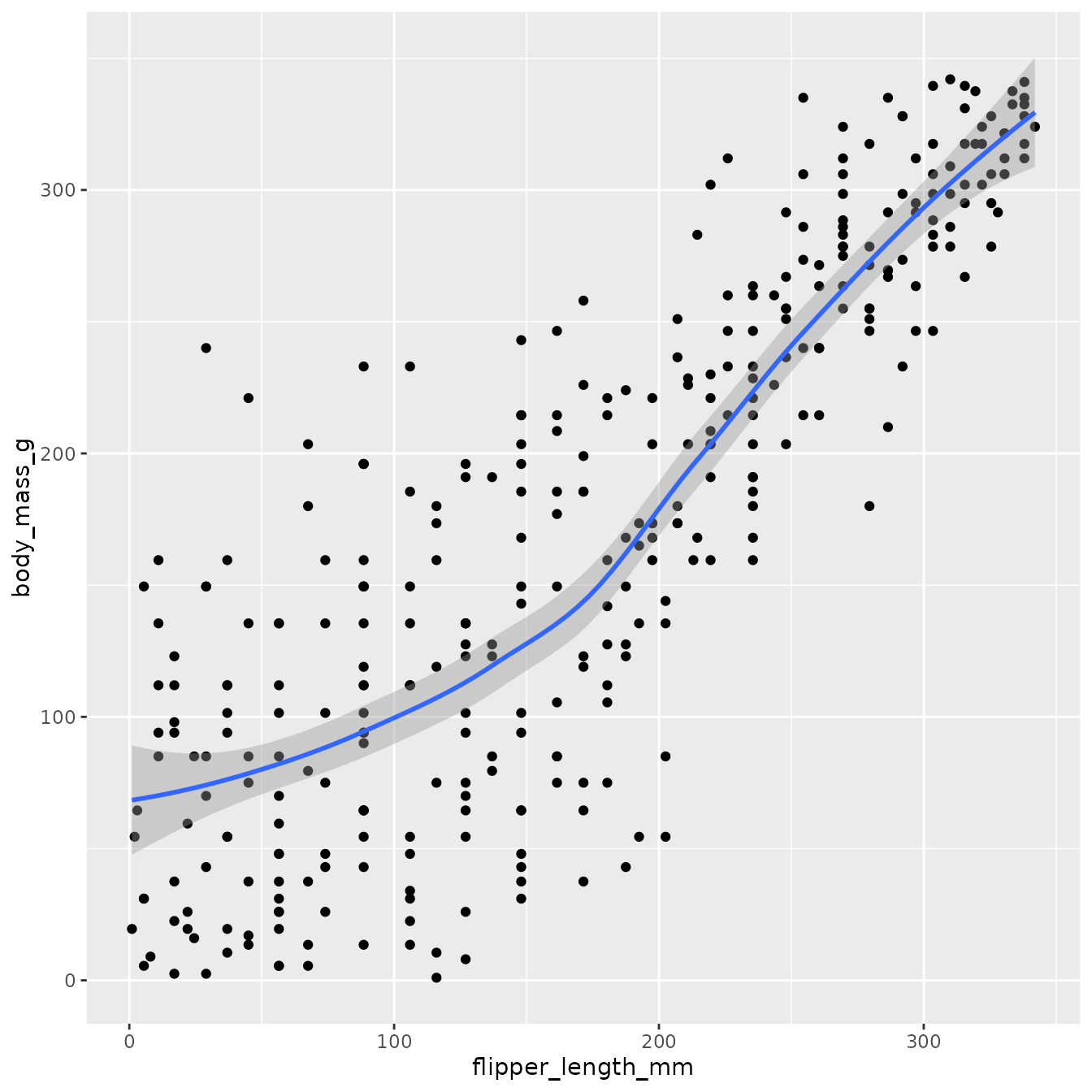
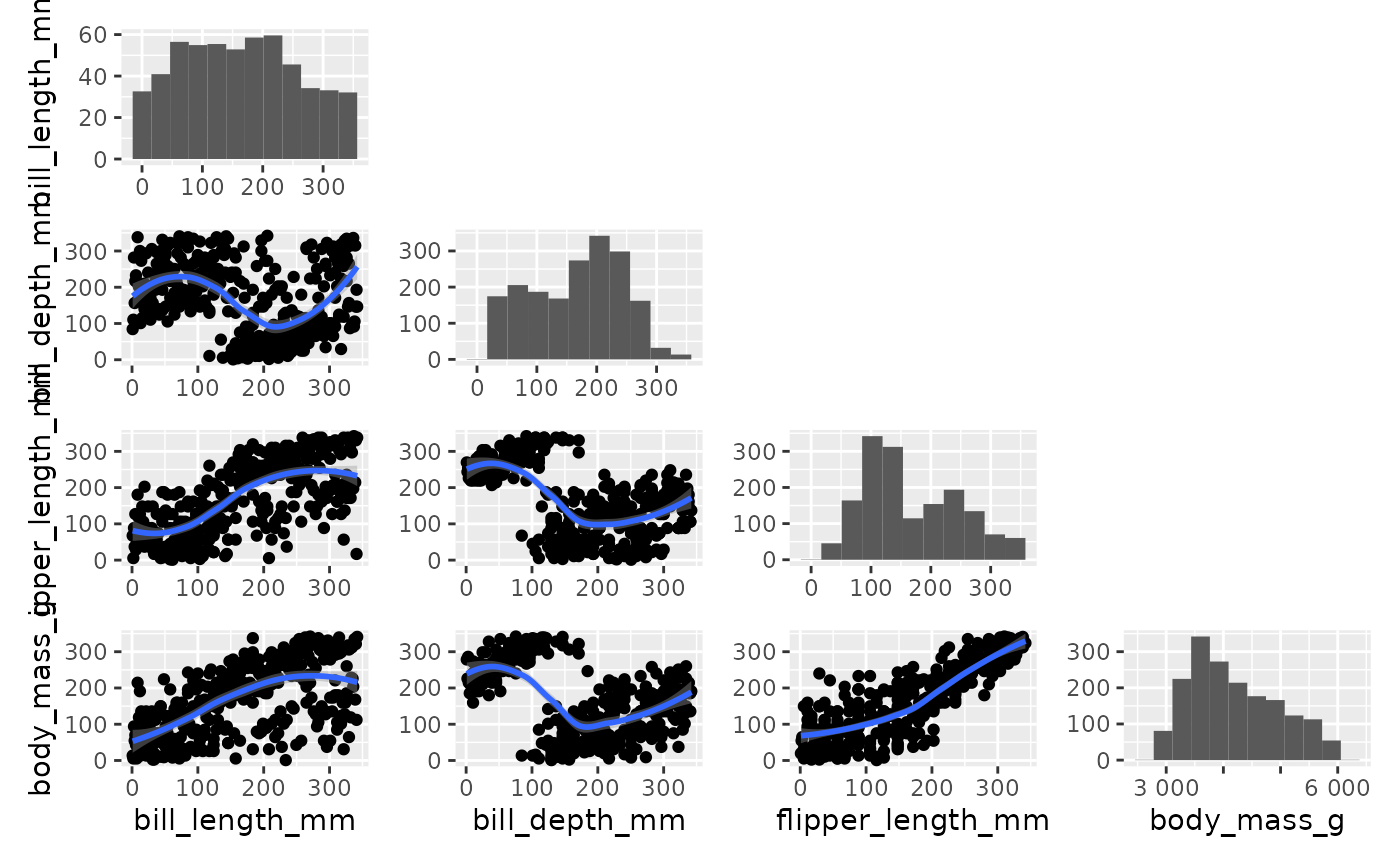
On the pairgrid down below we see that histogram are not in proportion.
pairgrid(
penguins,
map_lower=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
map_diag=pair_geom_histogram,
map_upper=NULL,
diag_share_lim=T, repeat_text=T,
common_ylim=function(data, y){return(c(min(rank(data[y])), max(rank(data[y]))))},
common_xlim=function(data, x){return(c(min(rank(data[x])), max(rank(data[x]))))}
)
#> Warning: Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y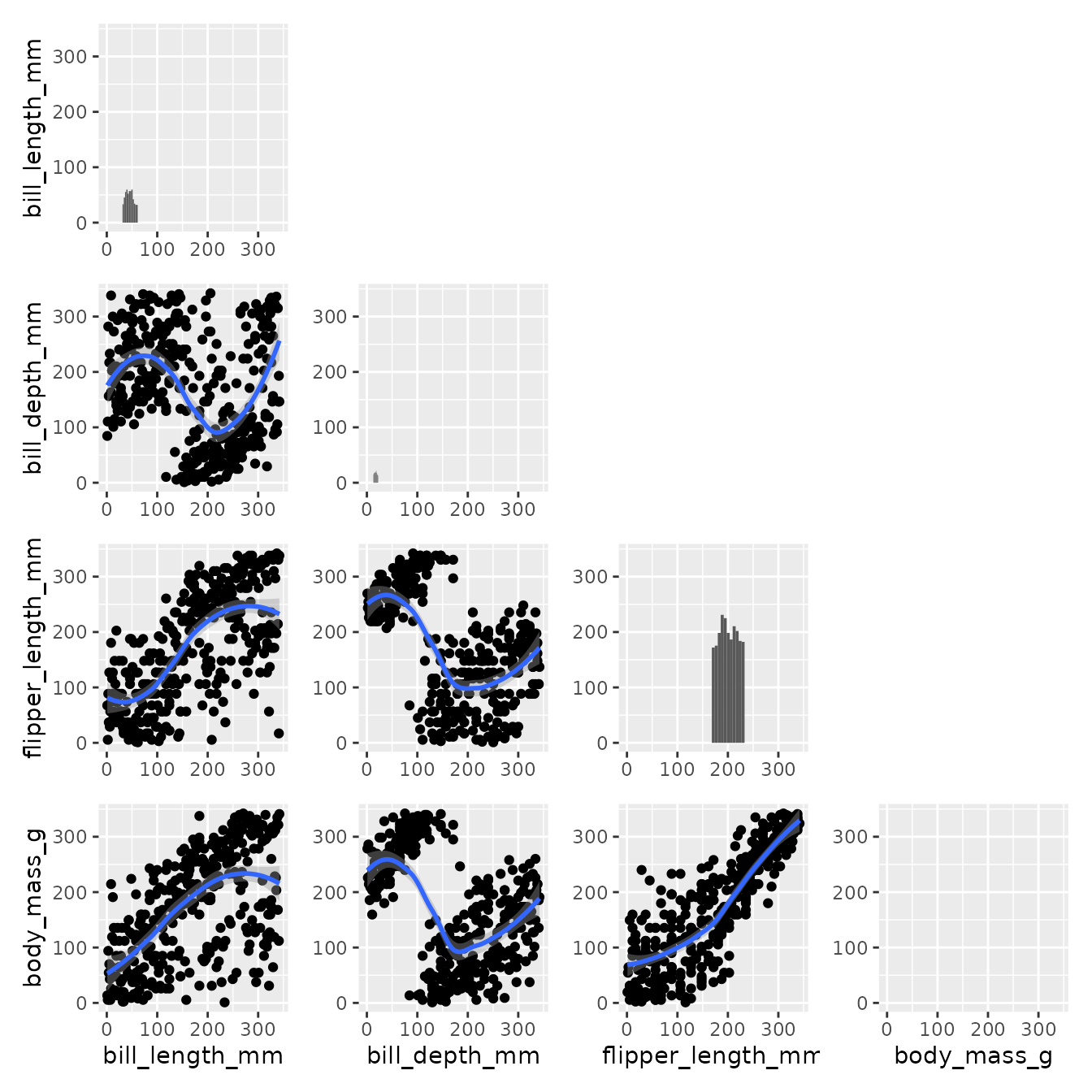
Down below, we leverage the surrounding information and min max scale the data on the x-axis and y-axis with respect to surroundings.
pairgrid(
penguins,
map_lower=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
map_diag=pair_geom_histogram,
map_upper=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
diag_share_lim=T, repeat_text=T,
common_xlim=function(data, x){
return(c(min(rank(data[x])), max(rank(data[x]))))
},
common_ylim=function(data, y){
return(c(min(rank(data[y])), max(rank(data[y]))))
},
diag_neighbour=c("l", "b", "t", "r")
)
#> Warning: Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y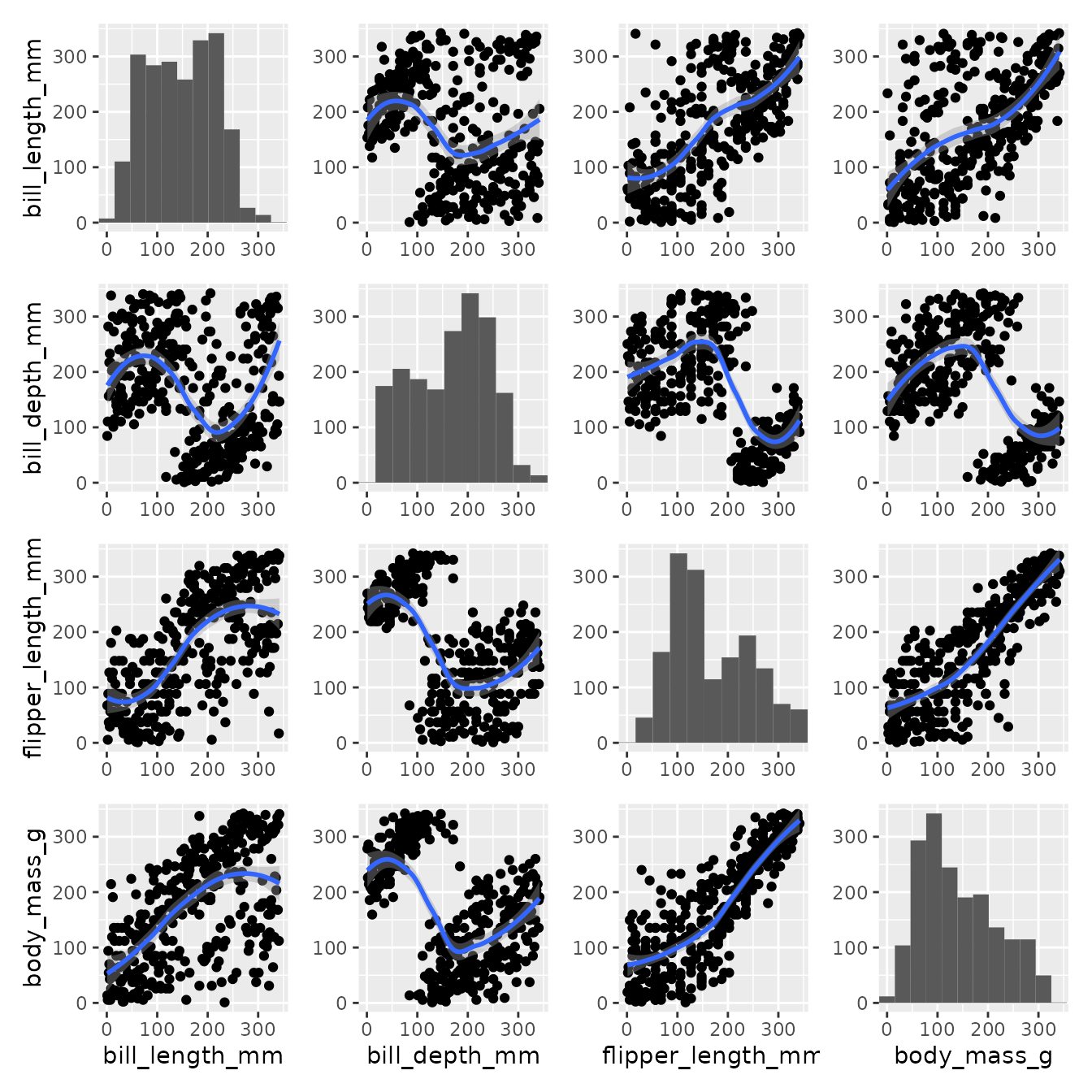
The down-side of the double min max scaling is interpretation which can be misleading. A note might be useful:
pairgrid(
penguins,
map_lower=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
map_diag=pair_geom_histogram,
map_upper=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
common_xlim=function(data, x){
return(c(min(rank(data[x])), max(rank(data[x]))))
},
common_ylim=function(data, y){
return(c(min(rank(data[y])), max(rank(data[y]))))
},
diag_neighbour=c("l", "b", "t", "r")
) + patchwork::plot_annotation(caption=element_text("Histograms' x and y axis were rescaled with respect to the surrounding plots' y and x limits"))
#> Warning: Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y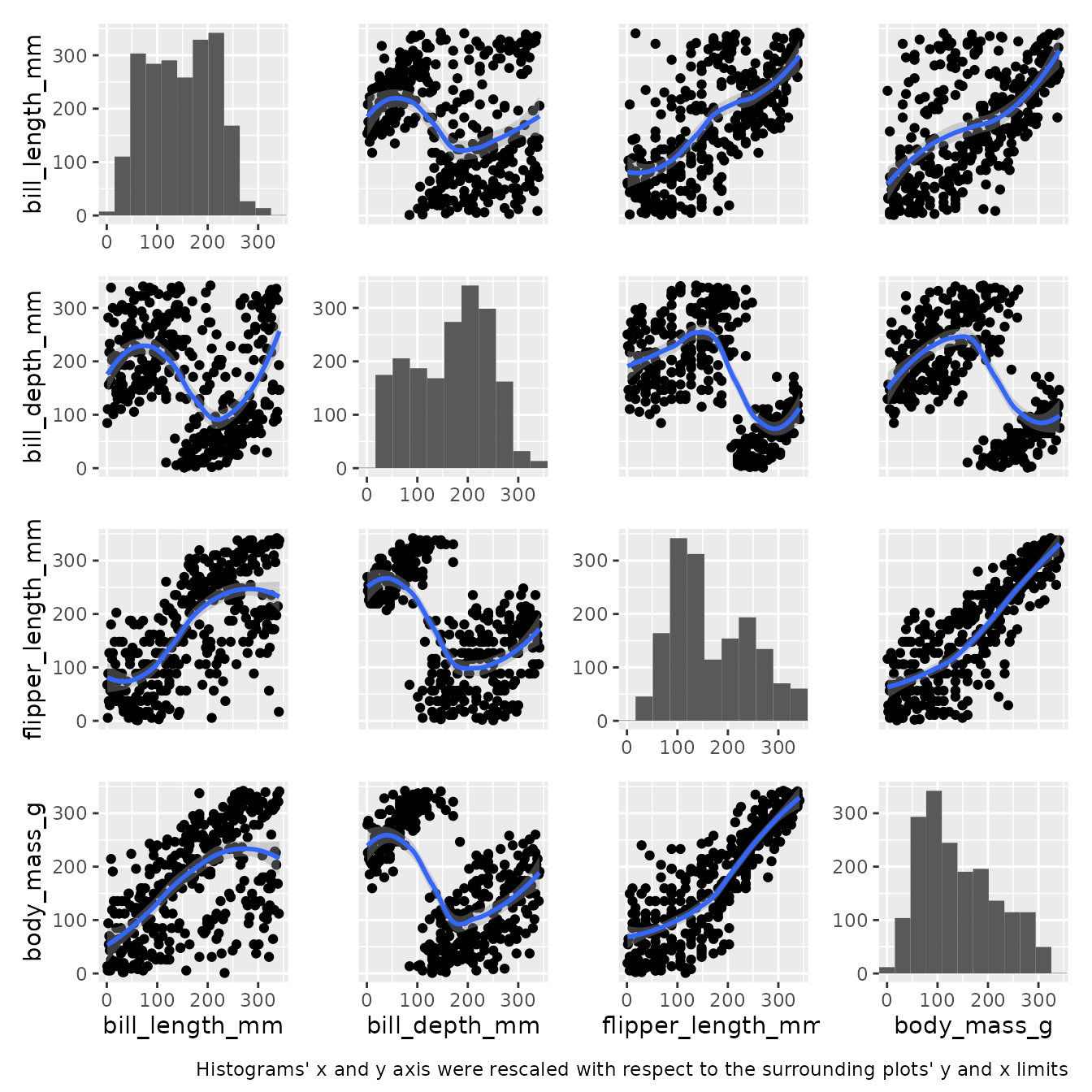
Another option for visualizing this kind of data without min max scaling is to allow misalignment of limits on diagonal only and display the text on the diagonal and border contigous subplots. Four arguments have to be specified, common_xlim=<func>, common_ylim=<func>, diag_share_lim=FALSE, text_on_diag=TRUE.
pairgrid(
penguins,
map_lower=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
map_diag=pair_geom_histogram,
map_upper=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
common_xlim=function(data, x){
return(c(min(rank(data[x])), max(rank(data[x]))))
},
common_ylim=function(data, y){
return(c(min(rank(data[y])), max(rank(data[y]))))
}, diag_share_lim=FALSE,
text_on_diag=TRUE
)
#> Warning: Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y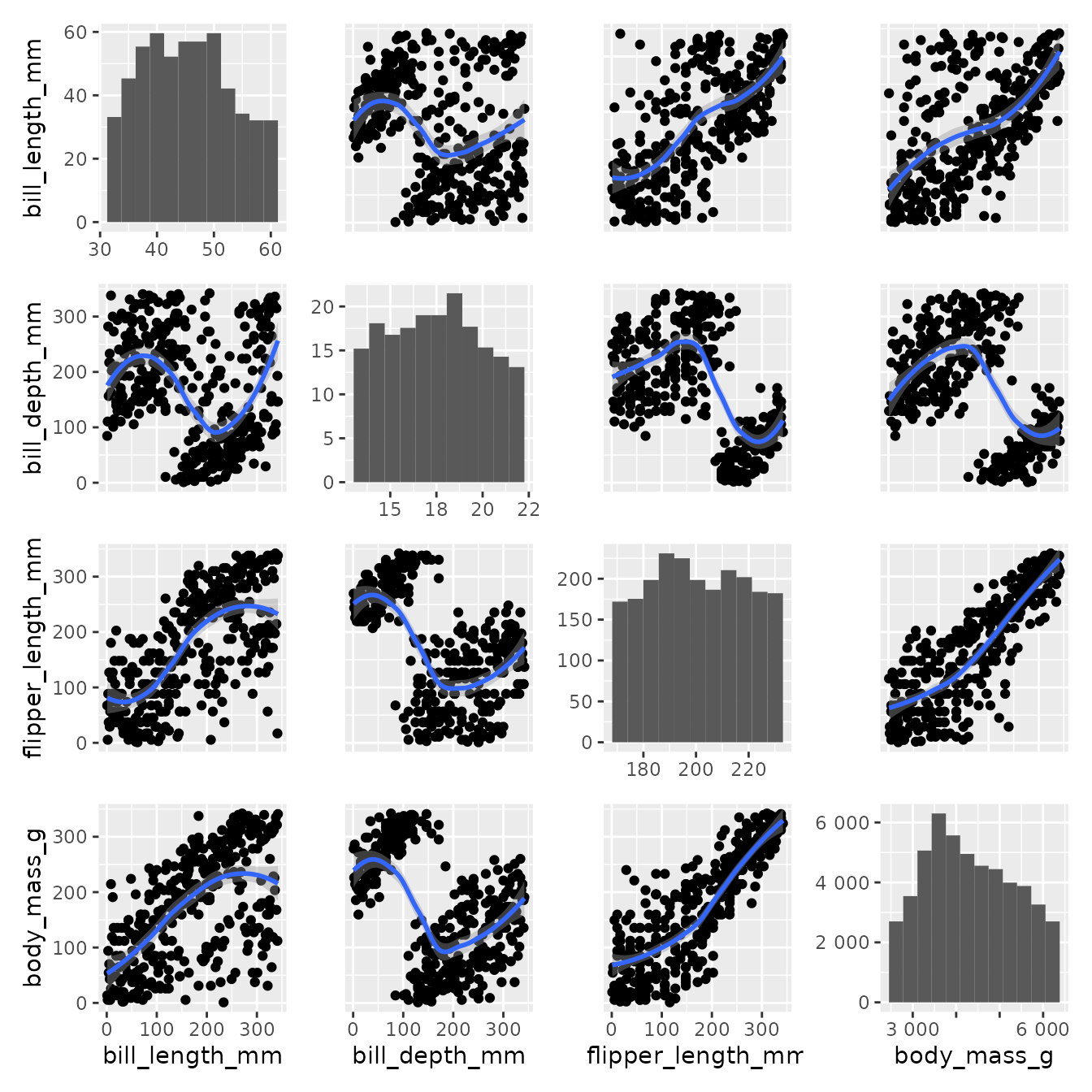
pairgrid(
penguins,
map_lower=pair_geom_rank_smooth,
map_diag=pair_geom_histogram,
map_upper=NULL,
diag_share_lim=F, repeat_text=T,
common_xlim=function(data, x){
return(c(min(rank(data[x])), max(rank(data[x]))))
},
common_ylim=function(data, y){
return(c(min(rank(data[y])), max(rank(data[y]))))
},
diag_neighbour=c("l", "b", "t", "r")
)
#> Warning: Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y
#> Ignoring unknown parameters: unit_y